Trending
Opinion: How will Project 2025 impact game developers?
The Heritage Foundation's manifesto for the possible next administration could do great harm to many, including large portions of the game development community.

Featured Blog | This community-written post highlights the best of what the game industry has to offer. Read more like it on the Game Developer Blogs or learn how to Submit Your Own Blog Post
Within this article I will be exploring power progression, how it is a fundamental element of game design, and why it taps into the human desire for growth and mastery.
September 6, 2024
.jpg?width=1280&auto=webp&quality=95&format=jpg&disable=upscale)
Within this article I will be exploring power progression, how it is a fundamental element of game design, and why it taps into the human desire for growth and mastery. I will presenting my own understanding and experiences as both a player and a game designer
Whether it's levelling up a character, acquiring new abilities, or unlocking powerful gear, the satisfaction of becoming stronger or more capable keeps players engaged and invested in the game world. Understanding the psychology behind power progression can help game designers create experiences that resonate with players on a deeper level, leading to more immersive and enjoyable games.
At the heart of power progression, in games, lies the delicate balance between intrinsic and extrinsic motivation. Intrinsic motivation drives players through the internal satisfaction of mastering skills, overcoming challenges, or uncovering stories. Some other common intrinsic motivators are exploration and curiosity. Detroit: Become Human relies quite heavily on these types of motivation; this game's story changes depending on the player's actions, using curiosity to drive players to replay the game and explore alternative versions of the story.
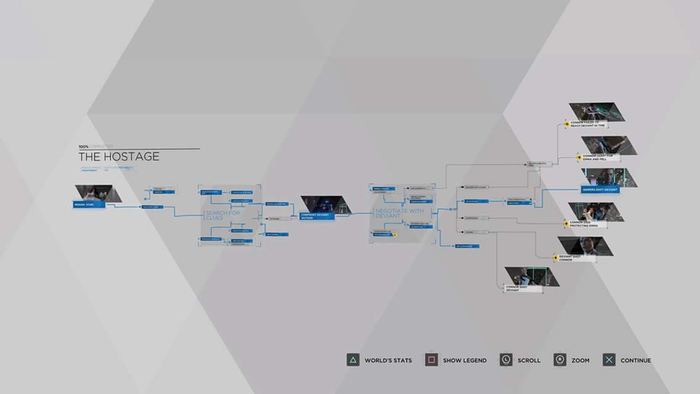
On the other hand, extrinsic motivation is fueled by external rewards like levelling up, earning loot, or gaining recognition from others. Many multiplayer competitive games motivate the player through their ranking systems and being able to showcase their rank as prestige, or unlockable skins.
Valorant and Call of Duty will award players with icons to represent either their mastery of the game, or overall play time. Turning an intrinsic motivator (mastery) into an extrinsic one (recognition).
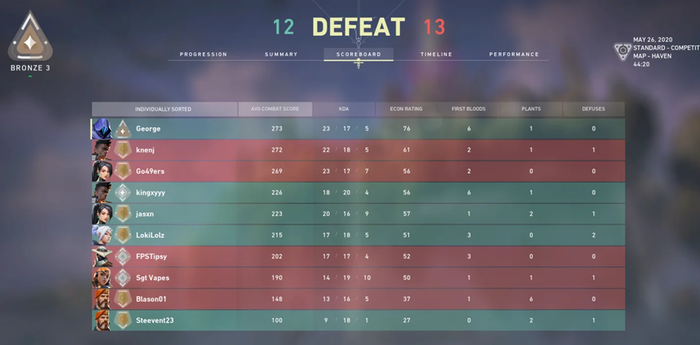
Ideally, the reward system within your game should be linked to the brain’s reward system, particularly the release of dopamine. When players achieve a goal, such as levelling up or acquiring a powerful item, the player should ideally feel a sense of accomplishment and be encouraged to continue playing. Conditioning the player to understand the importance of certain events through the use of sound, lighting or animations can help connect the idea of the triggering action as something positive and rewarding. The Soulsborne series is an excellent example of when to reward the player with dopamine. Slaying a boss will have them let out a final groan, begin to fade and the words of your victory appear, leaving you alone and in a now quiet boss arena, allowing the player to rejoice in the fact they overcame the obstacle.

The Legend of Zelda series also uses this feeling of build up when acquiring a new key item. The game sets the expectation that a large chest will contain something that will give you access to new areas of the game. It builds further emphasis on the importance of this item by combining several of the mentioned elements; having a musical jingle, playing an animation and drawing all focus on Link opening the chest.

Feedback loops are a fundamental concept in game design, especially in the context of power progression. A positive feedback loop occurs when success in the game leads to further success, creating a sense of momentum and growth. Open world games that have level-locked zones allow for the player to feel this sense of power increase; enemies that used to be tough are now easily dispatched and an area the player previously couldn’t have survived, now becomes the play area for them to explore.
Conversely, a negative feedback loop can be used to introduce challenges that prevent players from advancing too quickly, ensuring that the game remains engaging and balanced. Mario Kart uses a negative feedback loop with its item distribution system, the better your positioning within the race the weaker your item will be.
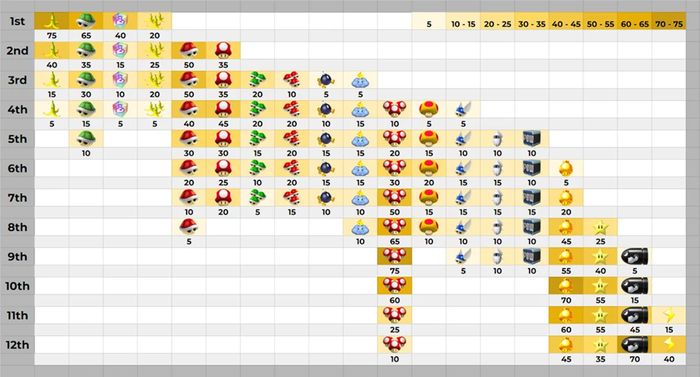
The core of an effective progression system lies in the balance between challenge and reward. If a game is too difficult, players may feel frustrated and disengaged; if it's too easy, the rewards can feel unearned, diminishing the sense of accomplishment. Striking the right balance means creating a difficulty curve that gradually increases, ensuring that players are constantly being tested but are also consistently rewarded for their efforts. This balance keeps players in a state of "flow", where the game is challenging enough to be engaging but not so difficult that it becomes discouraging. Within Left 4 Dead 2’s The Parish level, the director system will determine a path through the cemetery and how intense of a hoard to fight depending on how the players are progressing, aiming to keep the players in an appropriate state of flow whilst moving through the zone.

In any progression system, the pacing of rewards is crucial. Frequent small rewards keep players motivated, while larger, more significant milestones provide a sense of major achievement. However, periods of slower progression, or plateaus, can also play an important role. These moments of relative stasis build anticipation and make the eventual breakthrough more satisfying. By designing a progression system with well-placed milestones and intentional plateaus, game designers can keep players engaged and eager to continue their journey.
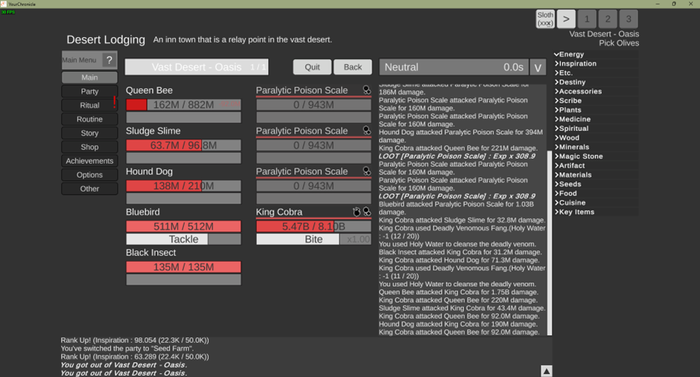
Your Chronicle, an incremental game, showcases this principle well. The player can progress through each area's minor dungeons, unlocking small amounts of content upon completion (minor milestones), however the story content will plateau unless the player switches gears to focus on increasing the strength of their creatures, allowing them to beat the area boss and unlock the next area of content (major milestone).
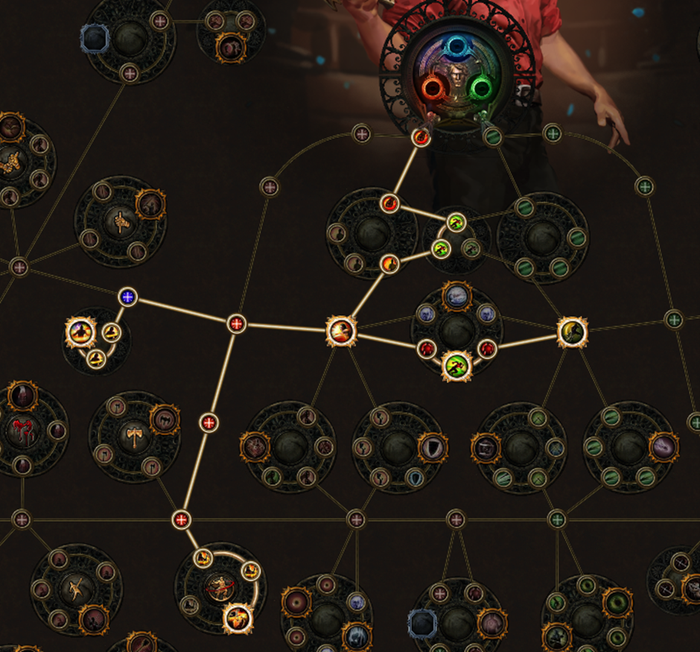
One of the most effective ways to enhance player engagement is by offering customisable progression paths. Whether through skill trees, branching storylines, or personalised upgrades, allowing players to choose how they progress through the game creates a deeper sense of ownership and investment in their character’s development. This personalisation not only makes the progression feel more meaningful but also caters to different playstyles, ensuring that a wide range of players can find satisfaction in their unique journey through the game.
Path of Exile’s skill tree will place the player on a different starting point depending on which character they start with, and as they player earns skill points they can move around the tree customising the build to whatever they would like.
Players start as beginners, often with limited abilities and knowledge, and gradually grow into experts who can overcome increasingly complex challenges. This progression mirrors many classic tales, where the protagonist evolves through trials and tribulations. By carefully pacing this growth, game designers can create a deep emotional connection between the player and their character, making each victory feel like a hard-earned step toward mastery. The satisfaction of seeing one’s skills develop over time is a key driver of long-term engagement.
Encountering new obstacles and setbacks requires players to measure, compare and adapt the strategies they had been using, allowing them to develop new strategies, eventually leading to learning and triumph. Forcing players to interact with a new item or ability increases their overall understanding and mastery of the game. Effective obstacle design encourages experimentation and enhances the player’s sense of achievement, turning moments of struggle into learning points.

Within my own game Deadbeat Wizard, the player must use their lightning spell to disable shielded enemies.
As players approach the endgame, the traditional power progression often slows or reaches its peak. However, maintaining player engagement at this stage is crucial. The endgame can introduce new forms of progression, such as mastery of advanced mechanics, social status within the game’s player community, or the pursuit of rare and prestigious rewards. By shifting the focus from growth to refinement, and from power to prestige, designers can create a satisfying conclusion to the player's journey while still offering goals to strive for. This approach ensures that the emotional investment in the game continues, even after the main progression is complete.
RPGs such as Baldur's Gate and Chrono Trigger are examples of how power progression can be integrated into the game's narrative and mechanics. Within Baldur’s Gate, the progression system is deeply tied to the world of Dungeons & Dragons, where players experience significant growth as they level up, gain new spells and acquire legendary gear. Chrono Trigger offers a unique take where the character progression is not only about becoming stronger but also about unlocking new abilities that allows the player to explore different eras and change the course of history. Both these RPGs demonstrate how progression can be used to enhance both gameplay and storytelling, making each milestone feel like a meaningful step within the player's journey.
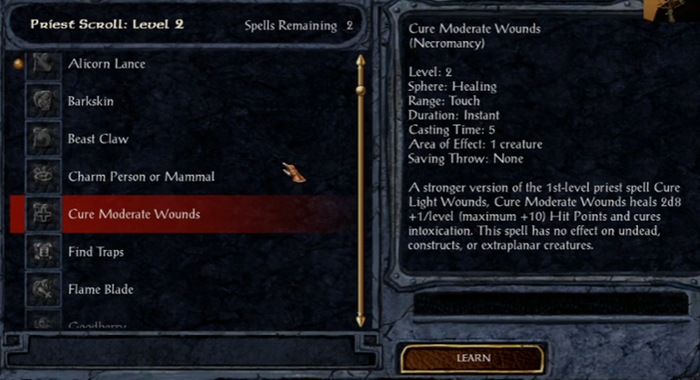
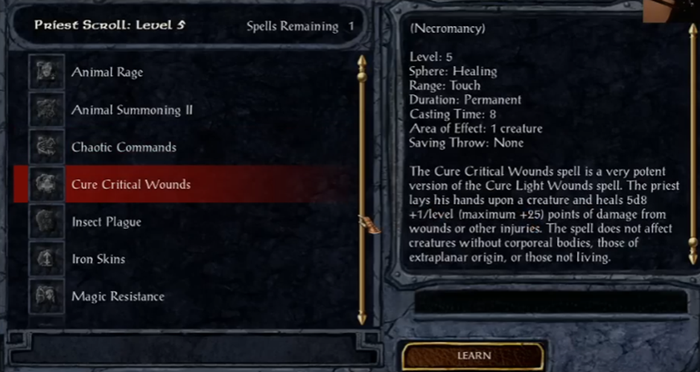
The increase of power when comparing a 2nd level healing spell to a 5th level healing spell within Baldur’s Gate.
Modern games have pushed the boundaries of traditional progression systems, introducing innovations that cater to diverse player preferences. For instance, adaptive difficulty systems dynamically adjust the game’s challenge based on the player's performance, ensuring a balanced experience that keeps players in their ideal "flow" state. Roguelites, on the other hand, offer a unique twist by using post-run progression, where each playthrough builds upon the last, creating a cycle of learning and improvement. These innovations highlight how contemporary game design continues to evolve, offering new ways to keep progression systems fresh and engaging.
Live service games, like Destiny 2 and Fortnite, have revolutionised power progression by introducing seasonal content that refreshes the player experience over time. These games keep players engaged through ongoing updates, new goals, and time-limited rewards that encourage regular play. Seasonal progression systems provide a sense of renewal and excitement, with each season offering new challenges and opportunities for growth and mastery of a new set of skills. This approach not only sustains long-term player interest but also creates a dynamic, ever-evolving game world where progression is constantly being redefined.



Fortnite Season 4 banners showcasing the new features and locations added within that chapter.
Power creep occurs when new content gradually raises the power ceiling, making older abilities, gear, or strategies less effective over time. This can lead to imbalance and frustration, as players may feel compelled to constantly chase the latest meta to remain competitive. To avoid power creep, designers can introduce horizontal progression, where new content offers different playstyles or abilities rather than simply increasing power. Additionally, seasonal resets or level caps can help maintain balance by ensuring that older content remains relevant and that progression feels fair and rewarding for all players.
One of the risks in designing power progression systems is falling into monotony, where players feel like they're simply grinding through repetitive tasks to achieve incremental gains. This can quickly lead to boredom and disengagement. To combat monotony, it's essential to introduce variety in the ways players progress. This could involve offering multiple types of challenges, incorporating narrative-driven progression elements, or providing different routes to reach similar goals. By keeping the progression experience dynamic and varied, designers can maintain player interest and help make each step in the journey feel fresh and exciting.

Skill level 92 is the halfway point in terms of experience to reach skill level 99 in RuneScape.
Player fatigue is a common issue in games with extensive power progression systems, particularly when players feel pressured to constantly grind for progression. This can lead to burnout and a diminished enjoyment of the game. To prevent fatigue, it's important to design progression systems that allow for breaks and downtime. Implementing features like daily or weekly caps on progression, offering non-progression-based activities, or introducing narrative pauses can give players a chance to recharge without feeling like they’re falling behind. By respecting players' time and providing a balanced pace of progression, designers can help maintain long-term player engagement and enjoyment.
Striking the right balance between challenge and reward is essential. When players feel that their progress is deserved and impactful, it deepens their connection to the game and enhances the sense of achievement with each milestone. Avoiding missteps like power creep or overly slow advancement ensures that the progression remains exciting and rewarding, encouraging players to continue their journey.
Innovation in power progression breathes new life into familiar systems, offering fresh experiences that keep players intrigued. Whether by revisiting classic mechanics or introducing entirely new ones, designers have the opportunity to create progression systems that resonate deeply, making each step forward feel significant and engaging.
And so in the end, power progression is far more than a method for increasing a player's capabilities; it's the driving force behind a game’s emotional and narrative depth. This system takes players on a journey of growth, where every challenge overcome and every skill mastered becomes a testament to their evolving prowess. The true power of progression lies in its ability to keep players engaged, motivated, and emotionally invested in their journey.
You May Also Like